Transpose of a matrix
A transpose of a matrix is obtained by interchanging rows of the original matrix with columns and vice-versa. The transpose of a matrix is the one whose rows are columns of the original matrix, i.e. if A and B are two matrices such that the rows of the matrix B are the columns of the matrix A then Matrix B is said to be the transpose of Matrix A. In other words, transpose of A[][] is obtained by changing A[i][j] to A[j][i]. It is very commonly used in mathematics as well as programming while multiplying two matrices.
Example
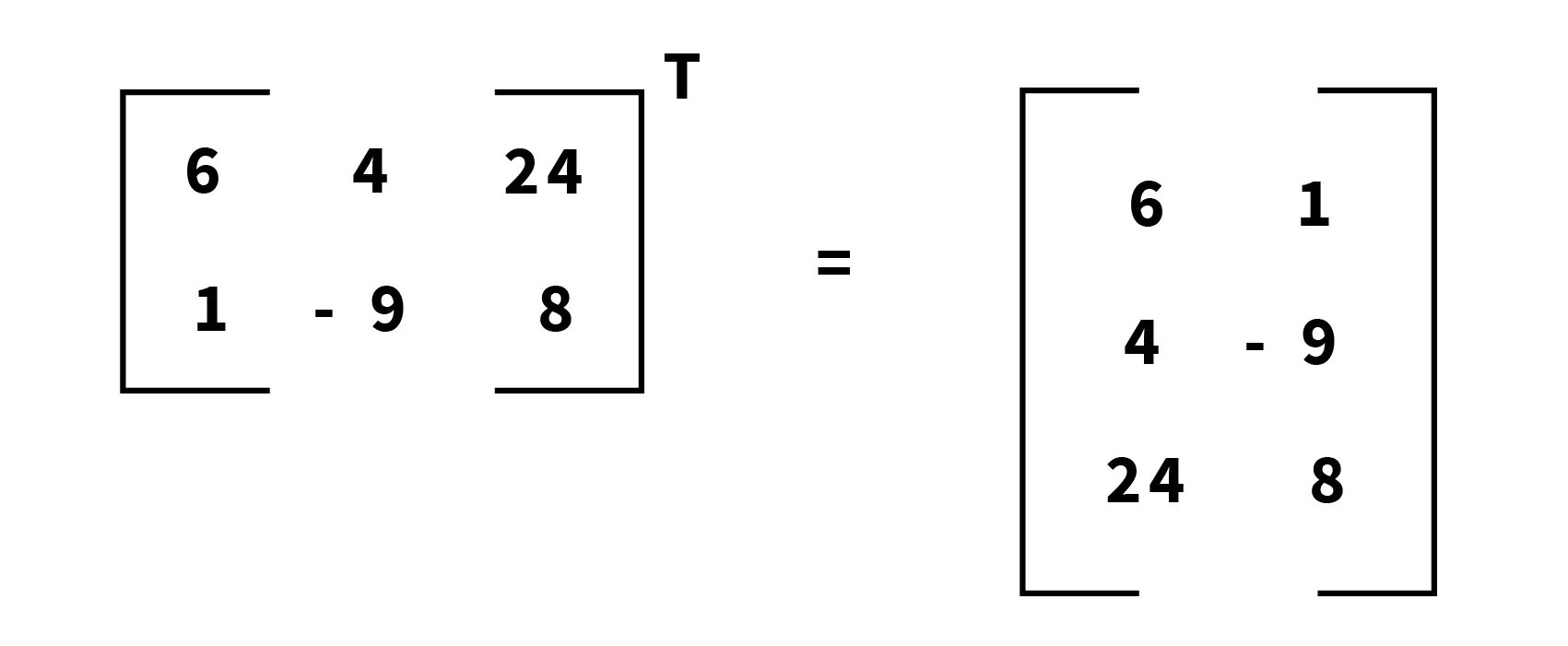
Here, the order of the original matrix is say 2x3 then the order of the transposed matrix would be 3x2, as shown in the figure above.
Algorithm
- Declare and initialize a 2-D array p[a][b] of order axb.
- Read the matrix p[a][b] from the user.
- Declare another 2-dimensional array t to store the transpose of the matrix. This array will have the reversed dimensions as of the original matrix.
- The next step is to loop through the original array and to convert its rows to the columns of matrix t.
- Declare 2 variables t and j.
- Set both i, j = 0
- Repeat until i<b.
- Repeat until j<a
- t[i][j] = p[j][i]
- j=j+1**
- i=i+1
- The last step is to display the elements of the transposed matrix t.
