Polynomial representation and addition using Linked List
A polynomial p(x) is the expression in variable x which is in the form (axn + bxn-1 + …. + jx+ k), where a, b, c …., k fall in the category of real numbers and 'n' is non negative integer, which is called the degree of polynomial.
An essential characteristic of the polynomial is that each term in the polynomial expression consists of two parts:
- Coefficient
- Exponent
Example :
10x2 + 26x, here 10 and 26 are coefficients and 2, 1 is its exponential value.
Points to keep in Mind while working with Polynomials :
- The sign of each coefficient and exponent is stored within the coefficient and the exponent itself.
- Additional terms having equal exponent is possible one.
- The storage allocation for each term in the polynomial must be done in ascending and descending order of their exponent.
Representation of polynomial :
Polynomial can be represented in the various ways. These are:
- Using array
- Using linked list
Polynomial using linked list:
We store each polynomial as a singly linked list where each node stores the exponent and coefficient in the data part and a reference to the next node as shown in the figure below. Their sum is then stored in another linked list
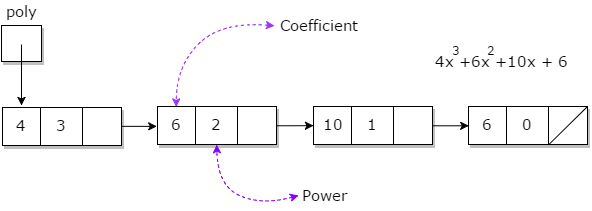
Procedure :
We store each polynomial as a singly linked list where each node stores the exponent and coefficient in the data part and a reference to the next node as shown in the figure below. Their sum is then stored in another linked list
Algorithm
Step 1: Start. Step 2: Define user defined datatype node consisting of int coefficient and exponent and a pointer next of type node. Step 3: Defining create function struct node* create(struct node* head, int co, int exp) Check if(head == Null) temp <- GetNode(node) temp.co <- co temp.exp <- exp temp.next <- Null Set head <- temp otherwise Set temp <- head while(temp.next ≠ Null) do temp <- temp.next flag <- GetNode(node) flag.co <- co flag.exp <- exp flag.next <- Null temp.next <- flag return head Step 4: Defining Addition function struct node* polyAdd(struct node *p1, struct node *p2, struct node *sum) Set poly1 <- p1 Set poly2 <- p2 Set result <- Null check if(poly1 ≠ Null AND poly2 == Null) Set sum <- poly1 Return sum else if(poly1 == Null AND poly2 ≠ Null) Set sum <- poly2 Return sum while(poly1 ≠ Null AND poly2 ≠ Null) do Check if(sum == Null) sum <- GetNode(node) Set result <- sum Otherwise result.next <- GetNode(node) Set result <- result.next Check if(poly1.exp > poly2.exp) Set result.co <- poly1.co Set result.exp <- poly1.exp Set poly1 <- poly1.next Check if(poly1.exp < poly2.exp) Set result.co <- poly2.co Set result.exp <- poly2.exp Set poly2 <- poly2.next Otherwise Set result.co <- poly1.co + poly2.co Set result.exp <- poly1.exp Set poly1 <- poly1.next Set poly2 <- poly2.next while(poly1 ≠ Null) do Set result.next <- GetNode(node) Set result <- result.next Set result.co <- poly1.co Set result.exp <- poly1.exp Set poly1 <- poly1.next while(poly2 ≠ Null) do Set result.next <- GetNode(node) Set result <- result.next Set result.co <- poly2.co Set result.exp <- poly2.exp Set poly2 <- poly2.next Set result.next <- Null Return sum Step 5: Defining Display function void display(struct node* head) Set temp <- head while(temp ≠ Null) do Display temp.co, temp.exp Set temp <- temp.next Step 6: Defining Main function Set p1 <- Null Set p2 <- Null Set sum <- Null Set flag <- 1 while(flag == 1) do Display “1: Create Polynomial 1” Display “2: Create Polynomial 2” Display “3: Perform Addition” Display “4: Exit” Read choice switch(choice) Case 1: Display “Enter coefficient for polynomial 1” Read co Display “Enter exponent for polynomial 1” Read exp Call create(p1, co, exp) Case 2: Display “Enter coefficient for polynomial 2” Read co Display “Enter exponent for polynomial 2” Read exp Call create(p2, co, exp) Case 3: Set sum <- call polyAdd(p1, p2, sum) Call display(sum) Case 4: Set flag <- 0 End switch Step 7: Stop
