Circular Queue Implementation
A Circular Queue in C is a data structure in which elements are stored in a circular manner. In Circular Queue, after the last element, the first element occurs.
A Circular Queue is used to overcome the limitation we face in the array implementation of a Queue. The problem is that when the rear reaches the end and if we delete some elements from the front and then try to add a new element in the queue, it says "Queue is full", but still there are spaces available in the queue.
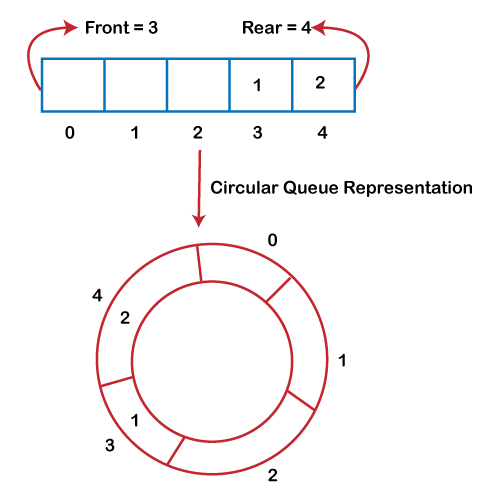
As we can see in the above image, the rear is at the last position of the Queue and front is pointing somewhere rather than the 0th position. In the above array, there are only two elements and other three positions are empty. The rear is at the last position of the Queue; if we try to insert the element then it will show that there are no empty spaces in the Queue. There is one solution to avoid such wastage of memory space by shifting both the elements at the left and adjust the front and rear end accordingly. It is not a practically good approach because shifting all the elements will consume lots of time. The efficient approach to avoid the wastage of the memory is to use the circular queue data structure.
Operations associated with a circular queue in C :
- isEmpty(): To check if the queue is empty
- isFull(): To check whether the queue is full or not
- dequeue(): Removes the element from the frontal side of the circular queue. In a circular queue, the element is always deleted from front position.
- Check whether queue is Full - Check ((rear == SIZE-1 && front == 0) || (rear == front-1)).
- If it is full then display Queue is full. If queue is not full then, check if (rear == SIZE - 1 && front != 0) if it is true then set rear=0 and insert element.
- enqueue(): It inserts elements to the end of the circular queue. In a circular queue, the new element is always inserted at Rear position.
- Check whether queue is Empty means check (front==-1).
- If it is empty then display Queue is empty. If queue is not empty then step 3.
- Check if (front==rear) if it is true then set front=rear= -1 else check if (front==size-1), if it is true then set front=0 and return the element.
- Front: Pointer element responsible for fetching the first element from the queue.
- Rear: Pointer element responsible for fetching the last element from the queue.
Algorithm
Queue follows the First-In-First-Out pattern. The first element is the first to be pulled out from the list of elements.
- Front and Rear pointers keep the record of the first and last element in the queue.
- At first, we need to initialize the queue by setting Front = -1 and Rear = -1
- In order to insert the element (enqueue), we need to check whether the queue is already full i.e. check the condition for Overflow. If the queue is not full, we'll have to increment the value of the Rear index by 1 and place the element at the position of the Rear pointer variable. When we get to insert the first element in the queue, we need to set the value of Front to 0.
- In order to remove the element (dequeue) from the queue, we need to check whether the queue is already empty i.e. check the condition for Underflow. If the queue is not empty, we'll have to remove and return the element at the position of the Front pointer, and then increment the Front index value by 1. When we get to remove the last element from the queue, we will have to set the values of the Front and Rear index to -1.
The most common queue implementation is using arrays, but it can also be implemented using lists.. Below here we have implemented queues using arrays in C.
