Binary Tree using Linked List
A binary tree is a tree data structure in which each node has at most two children, which are referred to as the left child and the right child.Every node excluding a root in a tree is connected by a directed edge from exactly one other node. This node is called a parent.
On the other hand, each node can be connected to arbitrary number of nodes, called children. Nodes with no children are called leaves, or external nodes. Nodes which are not leaves are called internal nodes. Nodes with the same parent are called siblings.
In the linked list representation, we cannot directly access the children of the current node unless we traverse the list.
- The depth of a node is the number of edges from the root to the node.
- The height of a node is the number of edges from the node to the deepest leaf.
- The height of a tree is a height of the root.
- A full binary tree.is a binary tree in which each node has exactly zero or two children.
- A complete binary tree is a binary tree, which is completely filled, with the possible exception of the bottom level, which is filled from left to right.
Important terms :
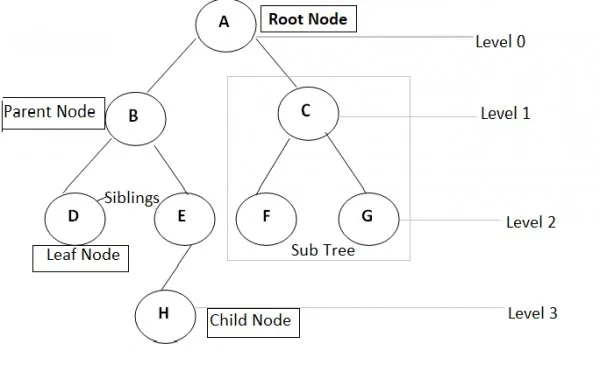
- Root - The node at the top of the tree is called root. There is only one root per tree and one path from the root node to any node.
- Parent - Any node except the root node has one edge upward to a node called parent.
- Child - The node below a given node connected by its edge downward is called its child node.
- Leaf - The node which does not have any child node is called the leaf node.
- Subtree - Subtree represents descendants of node.
Types of traversal :
- Inorder - (Left, Root, Right)
The left subtree is visited first, followed by the root, and finally the right subtree in this traversal strategy. Always keep in mind that any node might be a subtree in and of itself. The output of a binary tree traversal in order produces sorted key values in ascending order. - Preorder - (Root, Left, Right)
In this traversal method, the root node is visited first, then the left subtree, and finally the right subtree. - Postorder - (Left, Right, Root)
The root node is visited last in this traversal method, hence the name. First, we traverse the left subtree, then the right subtree, and finally the root node.
Algorithm
- Define Node class which has three attributes namely: data left and right. Here, left represents the left child of the node and right represents the right child of the node.
- When a node is created, data will pass to data attribute of the node and both left and right will be set to null.
- Define another class which has an attribute root.
Root represents the root node of the tree and initialize it to null. -
- It checks whether the root is null, which means the tree is empty. It will add the new node as root.
- Else, it will add root to the queue.
- The variable node represents the current node.
- First, it checks whether a node has a left and right child. If yes, it will add both nodes to queue.
- If the left child is not present, it will add the new node as the left child.
- If the left is present, then it will add the new node as the right child.
- Inorder() will display nodes of the tree in inorder fashion.
It traverses the entire tree then prints out left child followed by root then followed by the right child.
